Featured Articles

The Future of Nursing
Explore the future of the nursing and the benefits of pursuing a career in advanced practice nursing.

Professional Networking for Nurses
Broaden your horizon and advance your career through professional networking.

A Professional Nursing Portfolio
Develop a nursing portfolio for professional growth and career advancement.

Quick Links
This page is designed as a resource for nursing students and aspiring nurse professionals seeking career information, education, and job search assistance. All resources on this page are non-commercial in nature and free to use in any way you find beneficial. If you have any resources you'd like to see added to this page, please do not hesitate to contact us.To learn more about advancing your career in nursing select a topic below.
Nursing Employers by State
Below you'll find links to comprehensive directories of nursing employers for each state. The directories are designed to help nursing and health sciences students and professionals quickly locate and apply for jobs in cities and counties located throughout each state. To find immediate job openings or application information, simply click on the "apply" link to right of each institution. For general career information, click on the "learn more" link. If you position your cursor directly above the name of any organization listed in a directory, contact information, including phone number and address, will appear on the screen.
(Note: more directories are being added soon.)
- Virginia Nursing Employers

- Minnesota Nursing Employers
- Michigan Nursing Employers
- Georgia Nursing Employers
- Pennsylvania Nursing Employers
- Ohio Nursing Employers
- New York Nursing Employers
- Massachusetts Nursing Employers
- North Carolina Nursing Employers
- Texas Nursing Employers
- Florida Nursing Employers
- Illinois Nursing Employers
- California Nursing Employers
- Alabama Nursing Employers
Employment Information and Statistics
In this section we're going to present useful employment statistics for Registered Nurses. As Registered Nurses encompass the majority of nurse practitioners and nurse specialists, employment statistics for RNs most accurately reflect the nursing occupation as a whole. Figures for individual nursing specialties may vary.
As of 2013, there were approximately 2.8 million nurses employed nationwide. Of these, 29% were employed at hospitals and general medical centers, 8% worked in doctor's offices, 13% worked with home health companies, 9% worked in nursing care facilities and 15% worked in outpatient care centers. (See the industry employment charts below.)
The is a growing trend for nurses to work as nurse educators and teachers at colleges, universities, hospitals and in the community. Nurse educators have diverse backgrounds and work in many healthcare, medical and nursing environments.
The following chart shows those industries in the United States that employ the highest numbers of nurses:
Geographic Profile for Nursing Occupations
The maps and charts below show the states with the highest levels of employment, wages and location quotients for registered nurses and nursing professionals.
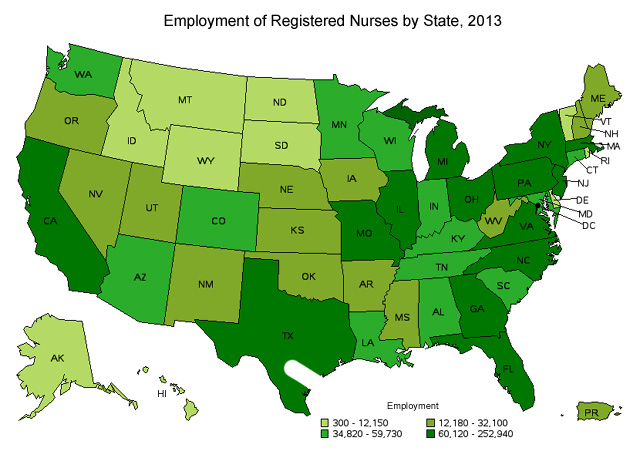 The table belows shows the states that employ the highest number of registered nurses. Taking the employment number and dividing it by the total population for the state will provide a ration of nurses to consumers. This ratio is useful indicator to considered when selecting where to practice as a nurse.
The table belows shows the states that employ the highest number of registered nurses. Taking the employment number and dividing it by the total population for the state will provide a ration of nurses to consumers. This ratio is useful indicator to considered when selecting where to practice as a nurse.
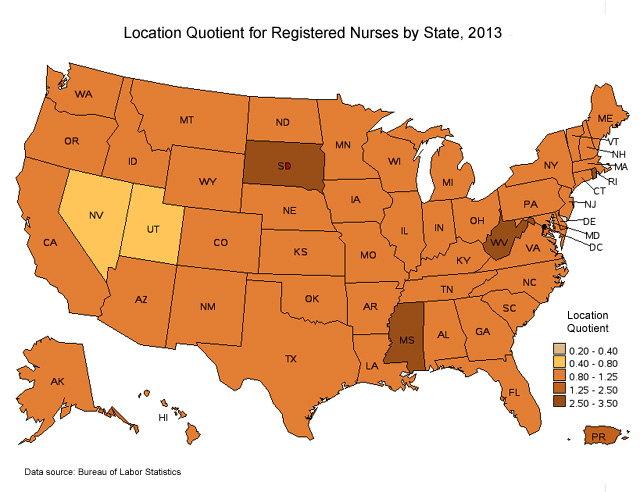
Below is a map of the location quotient for registered nurses on a state by state basis. The location quotient is the ratio of concentration of registered nurses employed in an individual state to the nation average concentration of registered nurses employed by state. Those states with a location quotient great than 1.0 employ a higher number of nurses than the national average.
As of 2013, there were approximately 2.8 million nurses employed nationwide. Of these, 29% were employed at hospitals and general medical centers, 8% worked in doctor's offices, 13% worked with home health companies, 9% worked in nursing care facilities and 15% worked in outpatient care centers. (See the industry employment charts below.)
The is a growing trend for nurses to work as nurse educators and teachers at colleges, universities, hospitals and in the community. Nurse educators have diverse backgrounds and work in many healthcare, medical and nursing environments.
The following chart shows those industries in the United States that employ the highest numbers of nurses:
| Industry | Employment | % of Industry Employment | Mean hourly way | Mean annual wage |
| Hospitals and General Medical | 1,553,100 | 29.46 | $34 | $70,600 |
| Doctor's Offices | 178,800 | 7.39 | $30 | $62,900 |
| Home Health Companies | 166,900 | 13.77 | $32 | $66,900 |
| Nurse Care Facilities | 142,500 | 8.6 | $30 | $62,000 |
| Outpatient Care Centers | 102,400 | 15.24 | $36 | $74,100 |
The maps and charts below show the states with the highest levels of employment, wages and location quotients for registered nurses and nursing professionals.
 The table belows shows the states that employ the highest number of registered nurses. Taking the employment number and dividing it by the total population for the state will provide a ration of nurses to consumers. This ratio is useful indicator to considered when selecting where to practice as a nurse.
The table belows shows the states that employ the highest number of registered nurses. Taking the employment number and dividing it by the total population for the state will provide a ration of nurses to consumers. This ratio is useful indicator to considered when selecting where to practice as a nurse.| State | Employment | Location quotient | Mean hourly way | Mean annual wage |
| California | 252,900 | .86 | $47 | $97,000 |
| Texas | 190,100 | .87 | $33 | $67,900 |
| New York | 169,800 | .98 | $36 | $75,5000 |
| Florida | 162,500 | 1.09 | $30 | $62,100 |
| Pennsylvania | 124,750 | 1.11 | $32 | $66,000 |

Salary and Wage Statistics
There are several factors that influence that wage a nurse can make. The largest factor influencing salary and wage is education and specialty. Obviously, a nurse anethetist with an advanced degree will make more than a registered nurse with a bachelor's degree working in general medicine. The second factor influence salary is location. A registered nurse working in South Dakota is likely to make about half of what a registered nurse in California will make working in the same position.
The map below shows the annual mean wage for registered nurses by state as of May 2013.
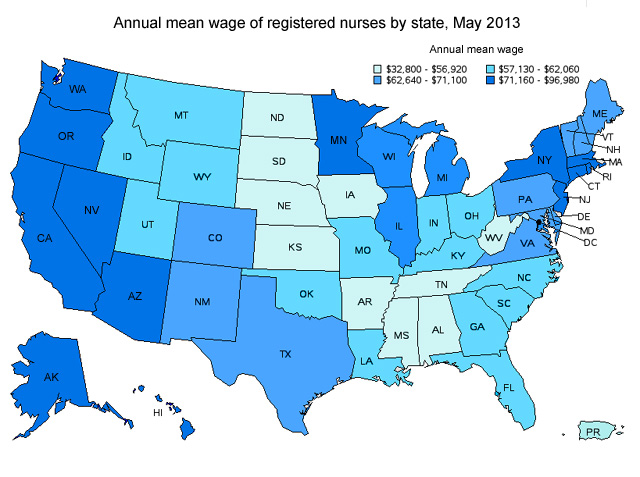 The table below lists the states that have the highest wage for registered nurses. Comparing this wage date to the cost of living index for each state will provide a real measure of how competitive each state is for compensation.
The table below lists the states that have the highest wage for registered nurses. Comparing this wage date to the cost of living index for each state will provide a real measure of how competitive each state is for compensation.
If you want to maximize your earning potential, then best place to work is in one of the major metropolitan areas in a top paying state. The table below lists the top paying metropolitan areas in the United States for registered nurses. (Not surprisingly, they're all in California.)
The map below shows the annual mean wage for registered nurses by state as of May 2013.
 The table below lists the states that have the highest wage for registered nurses. Comparing this wage date to the cost of living index for each state will provide a real measure of how competitive each state is for compensation.
The table below lists the states that have the highest wage for registered nurses. Comparing this wage date to the cost of living index for each state will provide a real measure of how competitive each state is for compensation.| State | Employment | Location quotient | Mean hourly way | Mean annual wage |
| California | 252,900 | .86 | $47 | $97,000 |
| Hawaii | 10,300 | .85 | $41 | $85,400 |
| Massachusetts | 79,300 | 1.21 | $40 | $83,700 |
| Alaska | 5,800 | .89 | $40 | $83,600 |
| Oregon | 28,500 | .87 | $39 | $80,400 |
| State | Employment | Location quotient | Mean hourly way | Mean annual wage |
| San Francisco-San Mateo-Redwood City, CA Metropolitan Division | 14,630 | .7 | $62 | $127,700 |
| San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA | 14,230 | .76 | $59 | $123,200 |
| Vallejo-Fairfield, CA | 3,230 | 1.32 | $58.50 | $121,670 |
| Oakland-Fremont-Hayward, CA Metropolitan Division | 20,100 | 1.00 | $58 | $121,040 |
| Sacramento--Arden-Arcade--Roseville, CA | 16,060 | .95 | $52 | $108,340 |
| Napa, CA | 1,660 | 1.26 | $50.70 | $105,360 |
| Modesto, CA | 3,670 | 1.16 | $50 | $104,900 |
| Santa Rosa-Petaluma, CA | 3,580 | 1.01 | $48 | $100,600 |
| Salinas, CA | 2,360 | .76 | $48 | $100,100 |
| Santa Cruz-Watsonville, CA | 1,380 | .80 | $47 | $98,300 |
Nursing Career Fields
Below we've compiled a comprehensive list of the most popular nursing career fields and disciplines. To learn more about a particular nursing career, simply click on the title in left hand column. To right of each career you'll find the minimum education requirements for entry-level positions in that particular field of nursing. (Note: you'll want to check with your state nursing board, as education, training and licensing requirements may vary by state.)
| Nurse Occupation | Education Requirements |
| Clinical Nurse Specialist | BSN, MSN and/or CNS Certificate |
| Nurse Anesthetist | BSN, MSN in Nurse Anesthesia |
| Nurse Educator | BSN, MSN (Preferred) |
| Nurse Midwife | BSN and CNM Certified |
| Nurse Practitioner | BSN, MSN, Doctorate (DNP) Preferred |
| Nurse Researcher | BSN, MSN, Ph.D. |
| Occupational Health Nurse | ADN or BSN |
| Pediatric Nurse | ADN or BSN, MSN with Oncology Specialization |
| Public Health Nurse | ADN, BSN or MSN (Preferred) |
| Registered Nurse (RN) | Diploma, ADN or BSN |
| Vocational/Licensed Practical Nurse | Diploma |
| Critical Care Nurse | ADN or BSN, CCRN Certificate |
| Emergency Nurse | Diploma, ADN or BSN (Preferred) |
| Hospice/Palliative Care Nurse | ADN or BSN (Preferred), Palliative Care Cert. |
| Labor & Delivery Nurse | Diploma, ADN or BSN (Preferred), Neonatal Cert. |
| Neonatal Nurse | BSN, Neonatal Training |
| Nephrology Nurse | ADN, BSN or MSN (Preferred) |
| Nurse Executive | BSN, MSN, Doctorate (Preferred) |
| Oncology Nurse | ADN or BSN, MSN with Oncology Training |
| Orthopaedic Nurse | Diploma, ADN or BSN (Preferred) & ONCB Certification |
| Perioperative (O.R.) Nurse | ADN or BSN |
| Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse | BSN and MSN |
| School Nurse | BSN and School Nurse Certificate |
| Staff Nurse | ADN or BSN |
Degree Paths
They're aren't many fields that offers such a diversity of educational and career paths as nursing. Before you launch your nursing career, we recommend spending some time familiarizing yourself with the various diploma, certificate and degree programs available. Which educational path you choose will depend on your career aspirations, and will impact your career opportunities down the road. Getting on the right educationl path now will help you avoid wasting time and money, and will prepare you for a successful nursing career.
- Diploma in Nursing
- LPN Degree
- LPN-to-RN
- Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN/ASN)
- LPN-to-BSN
- Bachelor's Degree in Nursing (BS/BSN)
- RN-to-BSN
- Accelerated Bachelor's in Nursing Degree (BSN)
- Master's of Science in Nursing (MSN)
- RN-to-MSN
- Doctor of Nursing (DNP)
- Doctor of Nursing Science (DNSc, DNS or DSN)
- Ph.D./Doctoral Nursing Degree
Accreditation
"Accreditation" is a process by which a school is evaluated and determined to meet certain minimum academic and professional standards. It is a seal of quality, essentially, an assurance that a reputable third-party accrediting agency has inspected the school and found it to exceed certain criteria.
In the United States, accreditation for nursing schools and programs are provided by two organizations: the Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education (CCNE) and the National League for Nursing Accrediting Commission (NLNAC). If a school or program is not accredited by one of these organizations, it doesn't necessarily mean that it provides substandard education. However, earning a degree from an accredited institution is a smart move, for several reasons.
It's much easier to transfer to another school or program after studying at an accredited school. There's no guarantee that credits earned at an unaccredited school will be accepted by your graduate school of choice, for example. Additionally, degrees from accredited institutions are more universally accepted by employers and organizations, which can make finding a job significantly easier.
Many merit-based and academic scholarships are only available to students of accredited nursing programs. Plus, students who attend an accredited nursing school are eligible for many federal financial aid options that are unavailable to students of unaccredited programs.
There are other organizations that accredit specialized nursing programs. For example, The American College of Nurse-Midwives Division of Accreditation (ACNM) evaluates and accredits midwifery programs, and The Council on Accreditation of Nurse Anesthesia Educational Programs (COA) accredits nurse anesthesia programs.
Being approved by a state board of nursing is NOT the same thing as being accredited. A school or program that has been approved by the state is licensed to prepare nursing students for the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). It does not necessarily mean that the school has been evaluated by an accrediting committee and shown to meet certain standards.
Before committing to any nursing program, check to see if it's accredited by either of the national nursing accrediting agencies. Usually, this information is available on the school's recruiting website or in the admissions office. Also important is how long the school has been accredited, and for how long the accreditation status is valid. Schools whose accreditation period is expiring must be reviewed by several committees, to ensure that the school has maintained its level of quality.
It's certainly possible to receive a quality education and enjoy a successful career in nursing by earning your degree at a non-accredited school. There are simply many advantages to earning a degree from an accredited program.
Company Information
About
Privacy Policy
Help
Contact Us
Submit a Resource
Copyright 2026 CareerProfiles.info, All rights reserved.
In the United States, accreditation for nursing schools and programs are provided by two organizations: the Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education (CCNE) and the National League for Nursing Accrediting Commission (NLNAC). If a school or program is not accredited by one of these organizations, it doesn't necessarily mean that it provides substandard education. However, earning a degree from an accredited institution is a smart move, for several reasons.
It's much easier to transfer to another school or program after studying at an accredited school. There's no guarantee that credits earned at an unaccredited school will be accepted by your graduate school of choice, for example. Additionally, degrees from accredited institutions are more universally accepted by employers and organizations, which can make finding a job significantly easier.
Many merit-based and academic scholarships are only available to students of accredited nursing programs. Plus, students who attend an accredited nursing school are eligible for many federal financial aid options that are unavailable to students of unaccredited programs.
There are other organizations that accredit specialized nursing programs. For example, The American College of Nurse-Midwives Division of Accreditation (ACNM) evaluates and accredits midwifery programs, and The Council on Accreditation of Nurse Anesthesia Educational Programs (COA) accredits nurse anesthesia programs.
Being approved by a state board of nursing is NOT the same thing as being accredited. A school or program that has been approved by the state is licensed to prepare nursing students for the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). It does not necessarily mean that the school has been evaluated by an accrediting committee and shown to meet certain standards.
Before committing to any nursing program, check to see if it's accredited by either of the national nursing accrediting agencies. Usually, this information is available on the school's recruiting website or in the admissions office. Also important is how long the school has been accredited, and for how long the accreditation status is valid. Schools whose accreditation period is expiring must be reviewed by several committees, to ensure that the school has maintained its level of quality.
It's certainly possible to receive a quality education and enjoy a successful career in nursing by earning your degree at a non-accredited school. There are simply many advantages to earning a degree from an accredited program.
Nursing Career Specialties
This section provides detailed descriptions of the most popular nursing careers in the United States along with links to relevant organizations, articles and resources that will help you learn more about each nursing discipline.
Advanced Practice Nurse
Advanced practice nurses hold master’s degrees in nursing and can be employed as the following specialists: Nurse Practitioner (NP), Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM), Clinical Nurse Specialist, RN First Assistant, Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA), and Nurse Psychotherapist.

Ambulatory Care Nurse
Ambulatory care nurses treat patients in facilities outside of hospitals, and they provide any requested assistance to their families. These specialists spend a lot of time educating patients, assisting individuals struggling with chronic pain, and helping patients with serious illnesses and diseases live independently.

Camp Nurse
Camp nurses treat and assist children at summer camps or other organized group activities. Additionally, these specialists treat children with serious health problems, including HIV, cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, and other debilitating health conditions.

Cardiac Care Nurse
Cardiac care nurses specialize in heart problems and treating patients struggling with cardiac disease. Even though these specialists typically work in hospitals where heart surgery is performed, they frequently assist patients at home recovering from bypass surgery, pacemaker surgery, or an angioplasty. Additionally, they work with patients requiring medication or close monitoring.

Cardiac Cath Lab Nurse
Cardiac cath lab nurses assist doctors diagnosing heart problems and performing interventional treatments, such as valvuloplasties, angioplasties, and cardiac catheterizations. Additionally, these specialists assist cardiologists implanting cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), pacemakers, and other devices. Since technology is constantly changing, they must remain updated on new technologies and procedures.

Case Management Nurse
Nurses assigned case management duties organize and oversee long-term patient care, ensuring patients receive all necessary treatments and care. For example, case management nurses assigned cancer patients would be responsible for coordinating oncologist visits, radiation and surgical treatments, and post-treatment care. These nurses typically specialize in various areas, including pediatrics, oncology, cardiology, AIDS, chronic pain management, etc.

Clinical Nurse Leader
Clinical nurse leaders are licensed registered nurses who hold master’s degrees in nursing (MSN). This is a relatively new nursing specialty. Clinical nurse leaders are responsible for minimizing patient care errors administered in clinical environments. These specialists supervise patient care activities to ensure people receiving medical care are being treated with modern technology and procedures.

Community Health Nurse
Community health nurses are employed at non-profit organizations, medical clinics, government agencies, and various other settings. They specialize in health problems affecting populations, assist underprivileged individuals, and work with families requiring public assistance. They organize public campaigns and classes to teach preventative healthcare, nutrition, and raise awareness about public health problems. Additionally, they collaborate with elected officials, doctors, teachers, and parents to assist underprivileged populations and address public health problems.

Complementary Health Nurse
Complementary health nurses specialize in holistic medicine. They administer alternative healthcare treatments, such as massage therapy, acupuncture, and special nutrition plans.

Correctional Facility Nurse
Correctional facility nurses work in correctional facilities. They treat inmates imprisoned within prisons, county jails, penitentiaries, and juvenile homes.

Dermatology Nurse
Dermatology nurses assist dermatologists. They also teach patients being treated for or recovering from skin disease how to properly care for themselves.

Developmental Disability Nurse
Developmental disability nurses treat and assist people diagnosed with mental or physical disabilities.

Diabetes Nurse
Diabetes nurses treat and assist people struggling with health problems related to diabetes, a disorder affecting insulin production. They also specialize in the endocrine system which includes the reproductive glands, hypothalamus, parathyroids, pituitary thyroid, pineal body, and adrenals.

Domestic Violence Nurse
Domestic violence nurses assist and treat victims of domestic abuse. They are typically employed at battered women shelters, police departments, and medical clinics. Many conduct research and participate in public advocacy to reduce domestic violence. This profession is also referred to as violence prevention, elder abuse, and child abuse nursing.

Ethics Nurse
Ethics nurses specialize in ethical issues within the nursing profession. They frequently sit on ethics committees at hospitals, insurance companies, and other facilities and work at law firms.

Family Nurse Practitioner
Family nurse practitioners hold master’s degrees and are licensed as registered nurses. Before being permitted to practice, they must certify by passing a national test. These specialists diagnose disease, arrange for diagnostic and lab tests, and some are permitted to prescribe medications. Since family nurse practitioners treat and care for patients of all ages, they possess the skills and knowledge to diagnose and provide care for various diseases and injuries.

Flight/Transport Nurse
Flight/transport nurses administer intensive care to critically injured or ill patients being transported to hospitals via ambulance or helicopter. Additionally, these specialists provide care to patients in less critical conditions being transported long distances by aircraft.

Forensic Nurse
Forensic nurses collaborate with police officers and criminal investigators conducting criminal investigations. They’re frequently called upon to investigate homicides, sexual assaults, abuse, and other crimes. Additionally, they treat and assist crime victims.

Gastroenterology Nurse
Endoscopy nurses, commonly known as gastroenterology nurses, assist doctors and provide nursing care to people struggling with digestive system problems. Common problems they treat include reflux, bleeding, abdominal pain, and cancers affecting digestive system organs.

Genetics Nurse
Genetics nurses administer nursing care to individuals diagnosed with genetic problems and diseases. They administer screenings, identify potential problems, treat disease, and assist child, adult, and elderly patients struggling with genetic disorders.

Geriatric/Gerontological Nurse
Geriatric and gerontological nurses provide nursing care to the elderly. These specialists are in high demand since over half of all hospitalized patients are 65 or older. Geriatric and gerontological nurses are primarily employed within hospitals and assisted living facilities. They have extensive training to prepare them for elderly patient care and teaching their patients how to live independently.

Gerontological Nurse Practitioner
Gerontological nurse practitioners specialize in elderly patient care. They hold master’s degrees and are licensed as registered nurses. These specialists are trained to diagnose and treat chronic and acute medical conditions. They frequently utilize holistic treatments to treat patients struggling with physical and mental health problems.

Gynecology/Obstetric Nurse
Gynecology and obstetric nurses specialize in women’s reproductive health. They treat women with reproductive issues, assist doctors, and teach adult and elderly women about preventative healthcare. These nurses often specialize as labor and delivery and perinatal nurses.

Health Policy Nurse
Nurses specializing in health policy work as analysts. They typically hold doctorate degrees and conduct research. Because of their expertise, health policy nurses frequently consult with elected officials, school administrators, and others to educate them about how health problems affect the public.

Hematology Nurse
Hematology nurses provide nursing care to patients diagnosed with leukemia, sickle-cell, hemophilia, or other blood related disorders. Since patients with these types of diseases need special care, they teach family members how to care for their loved ones. These blood-related diseases typically share similar characteristics with cancer, so hematology nurses frequently specialize in oncology.

Holistic Nurse
Holistic nurses utilize various treatments, including modern medical procedures, massage therapy, and nutrition plans to help patients recover from medical, psychological, and spiritual problems. Holistic nurses educate patients, so they’ll be empowered to take charge of their health.

Home Health Care Nurse
Home healthcare nurses administer nursing care to patients within their homes. They treat people recovering from serious injuries, the permanently disabled and elderly patients living independently. These specialists are also referred to as visiting nurses. Their work has improved the lives of untold numbers of people.

Independent Nurse Contractor
Independent nurse contractors provide their services to healthcare clinics where nurses are outsourced. They typically bill hourly. Nurse contractors have various specialties, and they can contract at physicians’ clinics, rehabilitation centers, assisted living facilities, physical therapy facilities, and home healthcare companies.

Infection Control Nurse
Infection control nurses recognize and eliminate infectious diseases rampant within medical clinics and the community. They gather data, educate staff members, and develop procedures to control the spread of infectious disease. They specialize in STDs, HIV, tuberculosis, and other infectious diseases common during hospital stays.

Informatics Nurse
Nurses specializing in informatics specialize in information technology utilized to manage records and deliver healthcare services. They’re currently in demand since paper form records are being digitized. They work with automated systems and sophisticated computer networks. They’re responsible for teaching nurses and other medical professionals how to utilize information technology and ensuring medical facilities are wired with modern networks.

Infusion Nurse
Infusion nurses, also known as intravenous nurses, administer fluids and mediations and assist patients who rely on arterial catheters. In addition to administering fluids, infusion nurses identify potential infections and drug interactions, keep tabs on patients, and fix problems. These specialists are employed at assisted living facilities, hospitals, and home healthcare companies.

Lactation Consultant
Nurses specializing in lactation assist women currently breastfeeding or experiencing complications. In addition to nursing care duties, these specialists work with elected officials to make the workplace and public facilities accommodating to breastfeeding mothers.

Legal Nurse Consultant
Nurses who offer legal consulting services assist attorneys with medical negligence cases and evaluate medical records.

Life Care Planning Nurse
Nurses specializing in life care planning assist severely injured patients recovering from serious burns, head trauma, spinal cord injuries, and other serious injuries. They work with patients, their family members, doctors, and lawyers to develop plans designed to address healthcare costs, future treatments, and other issues affecting patients’ wellbeing. To effectively do this, they must understand what type of treatments and care patients with specific injuries require. Additionally, these nurses must advocate on patients’ behalf since they often struggle expressing themselves. These specialists frequently work outside of hospitals as consultants for government agencies, courts, and private companies.

Long-term Care Nurse
Long-term care nurses treat patients with chronic diseases or severe disabilities. They typically work with elderly and disabled individuals. Long-term care is also known as sub-acute care.

Managed Care Nurse
Managed care nurses specialize in preventative care. They teach patients how to properly take care of their health to minimize healthcare expenses. They work with managed care healthcare providers to reduce expenses and provide more efficient care.

Medical-Surgical Nurse
Medical/surgical nurses are licensed registered nurses employed in assisted living facilities, hospitals, and other medical clinics where patients preparing and recovering from surgery are housed. Additionally, they assist patients with chronic pain being treated with medication.

Military and Uniformed Service Nurse
Military nurses serve in the military and care for service members in the Marines, Navy, Air Force, and Army. They also work for public health agencies.

Neonatal Intensive Care Nurse
Neonatal intensive care nurses treat premature or ill infants. They also assist mothers with any assistance while their newborns receive treatment.

Neuroscience Nurse
Neuroscience nurses specialize in nervous system disorders. They treat people with spinal cord injuries, severe brain trauma, seizures, and other nervous system injuries or diseases.

Nurse Attorney
These nurses hold law degrees. They frequently represent doctors and other medical specialists in court and collaborate with elected officials to develop new policies.

Nursing Legistlator
These professionals work for municipal, state, and federal government agencies. They work closely with politicians to formulate health policies to address rising healthcare costs, expanding coverage to underprivileged individuals, and other important health issues.

Nursing Manager/Administrator
Nurse managers and administers are typically experienced managers with nursing administration or business degrees. These professionals hold high-level positions at hospitals and medical clinics. They’re responsible for overseeing hospital nursing operations.

Ophthalmic Nurse
Ophthalmic nurses treat patients struggling with vision problems, such as glaucoma, blindness, cataracts, and other vision disorders.

Otorhinolaryngology Nurse
Otorhinolaryngology nurses assist and treat patients being treated for ear, nose, and throat problems. They also prepare patients for surgery. This field is also referred to as head and neck nursing.

Pain Management Nurse
Pain management nurses evaluate, assist, and monitor patients suffering with chronic pain. Pain management is also known as the fifth vital sign. They teach patients proper pain management techniques and monitor patients during pain management treatments. Nurses specializing in pain management are considered advanced practice nurses and pain management specialists since they have completed graduate-level education. Many pain management specialists certify in advanced oncology and palliative care.

Pediatric Endocrinology Nurse
Pediatric endocrinology nurses treat children diagnosed with endocrine system disorders and provide support to their families. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Children with endocrine system problems often begin puberty later in life and struggle with weight problems, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances.

Perianesthesia Nurse
Perianesthesia nurses assist patients in recovery rooms recovering from sedation following surgery. They get patients ready for surgery, monitor sedated patients, and help patients recovering from anesthesia.

Perinatal Nurse
Perinatal nurses administer nursing care to pregnant women, women in labor, and new mothers. They also provide support to women’s family members. These nurses spend a lot of time teaching mothers about proper prenatal care, comforting women struggling through labor, and teaching women how to care for newborns. Perinatal nurses are also called OB nurses, women’s health nurses, postpartum nurses, and couplet care nurses.

Plastic Surgery Nurse
Nurses employed in plastic surgery clinics assist patients preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from plastic surgery. They assist plastic surgeons performing all types of surgeries, including facial reconstruction surgery, dermabrasion, rhinoplasty, and other elective and necessary procedures.

Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
Psychiatric nurses are also known as mental health nurse practitioners. These specialists have advanced training and are licensed as registered nurses. Psychiatric nurse practitioners administer various psychiatric treatments and access patients for mental health problems. They assist patients struggling to manage mental health problems, and they provide preventative mental healthcare by teaching patients how to properly manage stress. These specialists are employed at psychiatric hospitals, addiction rehabilitation centers, and private clinics.

Pulmonary Care Nurse
Pulmonary care nurses treat patients with lung problems, such as asthma, tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, and individuals being taken off ventilators. These nurses work within hospitals in critical care and intensive care units, but they also work with patients at home struggling with emphysema, lung cancer, and other lung diseases.

Quality Improvement Nurse
Nurses specializing in quality improvement are responsible for improving nursing care at hospitals and other medical facilities. To do this, they evaluate current procedures, conduct patient surveys, and interview staff members. Once assessments are completed, these professionals develop new policies to be implemented within intensive care units, assisted living facilities, oncology clinics, etc.

Radiology Nurse
Radiology nurses assist patients receiving radiation treatment and being diagnosed with radiation imaging technology, such ultrasound technology and MRIs. Radiology nurses are also called cardiac catheterization lab nurses.

Rehabilitation Nurse
Rehabilitation nurses assist disabled patients and those recovering from serious injuries live independently. They also provide support to family members with disabled loved ones. Rehabilitation nurses also work in assisted living clinics to care for people unable to live independently.

Reproductive Nurse
Nurses specializing in reproductive health provide medical care and education to individuals with reproductive disorders, fertility problems, and other reproductive issues. These specialists are primarily located at fertility clinics where families are matched with egg donors and couples struggling with fertility problems receive counseling.

Rheumatology Nurse
Rheumatology nurses specialize in and care for patients with rheumatoid diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Lyme disease, fibromyalgia, lupus, spondylitis, and myositis. These nurses are responsible for assessing blood work and responses to pain, treating flares and symptoms, counseling patients, and determining whether patients are responding to medication.

Rural Nurse
Nurses practicing in rural settings treat patients living in scarcely populated and isolated regions. Frequently, rural areas lack doctors and healthcare resources. As a result, nurses are often responsible for providing care to people living in rural areas. To encourage nurses to work in rural settings, government agencies often offer tuition and loan repayment assistance.

Sub-acute Nurse
These specialists offer comprehensive nursing care to individuals requiring hospitalization for acute injuries and diseases. Most the time, this type of care lasts longer than long-term and assisted living care, but shorter than acute treatments.

Substance Abuse Nurse
Nurses specializing in substance abuse work at rehabilitation clinics where people undergoing treatment for drug and alcohol addiction are housed. They supervise patients receiving medications, provide routine nursing care, and offer emotional support to recovering addicts.

Supplemental/Agency Nurse
Nurses employed at nursing agencies work temporarily at hospitals and other medical facilities with staffing shortages.

Surgical Nurse
Surgical nurses assist patients preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from surgery. The following are specialists in this field: scrub nurses, specialists who sterilize surgical tools; RN first assistants, specialists who administer patient care during surgery; and circulating nurses, specialists with patient care duties in non-sterile settings.

Telemetry Nurse
Telemetry nurses specialize in technology designed to measure blood pressure, EKGs, blood-oxygen levels, and heart rate. They’re responsible for linking patients to this technology. After patients are linked to the technology, data about vital signs appear on computer screens for nurses and doctors to review. Telemetry nurses are responsible for analyzing and making judgments from the data.

Telephone Triage Nurse
Telephone triage nurses offer support to patients and other individuals requiring medical information via telephone. They’re frequently required to make judgments about the type of assistance people need after brief conversations. Telephone triage nurses are trained to understand when people need immediate medical care so unnecessary ambulance and emergency responses are minimized.

Toxicology Nurse
Toxicology nurses assistant patients undergoing detox treatments and requiring medical assistance following poison ingestion. These specialists often monitor patients for extended periods of time, conduct diagnostic and lab tests, and assist doctors treating poison victims. Additionally, toxicology nurses teach people how to avoid being exposed to toxic chemicals and compounds. These specialists must work well under stress since they frequently respond to life and death emergencies.

Transcultural Nurse
Transcultural nurses provide nursing care to immigrants, foreign refuges, and minorities. They typically understand the cultural values and beliefs of foreign nationals, so they understand how to administer care in a way that does not violate cultural and religious values.

Transplant Nurse
Transplant nurses assist people preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from organ transplants. They also work with living-donors preparing for surgery and the family members of organ transplant recipients. Transplant nurses coordinate nursing care for people receiving transplants and recovering from surgery. They also teach patients how to maintain good health following an organ transplant.

Trauma Nurse
Trauma nurses administer emergency treatment and care to people being treated for severe injuries. They monitor vital signs and notify doctors when emergency and life-saving treatments are needed.

Triage Nurse
Triage nurses are typically assigned to emergency rooms. They’re responsible for accurately and rapidly determining the type of treatment patients admitted to emergency rooms require. To do this, they must have exceptional analytical and judgment skills. Triage nurses must also be able to work effectively under pressure.

Urologic Nurse
Urologic nurses provide nursing care to patients with urologic disorders and diseases. They respond to acute disorders and treat patients struggling with chronic pain. They conduct exams, assess results from diagnostic tests, assist urologists treating bladder disorders, including incontinence, and educate patients about preventive healthcare.

Veterans Affair Nurse
Nurses employed with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) work at veterans’ hospitals, outpatient clinics, assisted living facilities, and other medical clinics where veterans receive medical care. Various nursing specialists, including registered nurses, clinical nurse specialists, APNs, NAs, LPNs, and nurse anesthetists are employed by the VA. In addition to treating veterans with health problems, they teach those with permanent disabilities how to live independently. Many VA nurses provide hospice care.

Wound & Ostomy Nurse
Wound and ostomy nurses assist patients requiring medical care for stomas, draining wounds, pressure and vascular wounds, fistulas, and neuropathic wounds. Additionally, they teach patients requiring special medical assistance how to manage these health disorders.

- Advanced Practice Nurse
- Ambulatory Care Nurse
- Camp Nurse
- Cardiac Care Nurse
- Cardiac Cath Lab Nurse
- Case Management Nurse
- Clinical Nurse Leader
- Community Health Nurse
- Complementary Health Nurse
- Correctional Facility Nurse
- Dermatology Nurse
- Developmental Disability Nurse
- Diabetes Nurse
- Domestic Violence Nurse
- Ethics Nurse
- Family Nurse Practitioner
- Flight/Transport Nurse
- Forensic Nurse
- Gastroenterology Nurse
- Genetics Nurse
- Geriatric/Gerontological Nurse
- Gerontological Nurse Practitioner
- Gynecology/Obstetric Nurse
- Health Policy Nurse
- Hematology Nurse
- Holistic Nurse
- Home Health Care Nurse
- Independent Nurse Contractor
- Infection Control Nurse
- Informatics Nurse
- Infusion Nurse
- Lactation Consultant
- Legal Nurse Consultant
- Life Care Planning Nurse
- Long-term Care Nurse
- Managed Care Nurse
- Medical-Surgical Nurse
- Military and Uniformed Service Nurse
- Neonatal Intensive Care Nurse
- Neuroscience Nurse
- Nurse Attorney
- Nurse Legislator
- Nursing Manager/Administrator
- Ophthalmic Nurse
- Otorhinolaryngology Nurse
- Pain Management Nurse
- Pediatric Endocrinology Nurse
- Perianesthesia Nurse
- Perinatal Nurse
- Plastic Surgery Nurse
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Pulmonary Care Nurse
- Quality Improvement Nurse
- Radiology Nurse
- Rehabilitation Nurse
- Reproductive Nurse
- Rheumatology Nurse
- Rural Nurse
- Sub-acute Nurse
- Substance Abuse Nurse
- Supplemental/Agency Nurse
- Surgical Nurse
- Telemetry Nurse
- Telephone Triage Nurse
- Toxicology Nurse
- Transcultural Nurse
- Transplant Nurse
- Trauma Nurse
- Triage Nurse
- Urologic Nurse
- Veterans Affair Nurse
- Wound & Ostomy Nurse
Advanced practice nurses hold master’s degrees in nursing and can be employed as the following specialists: Nurse Practitioner (NP), Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM), Clinical Nurse Specialist, RN First Assistant, Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA), and Nurse Psychotherapist.
Ambulatory Care Nurse
Ambulatory care nurses treat patients in facilities outside of hospitals, and they provide any requested assistance to their families. These specialists spend a lot of time educating patients, assisting individuals struggling with chronic pain, and helping patients with serious illnesses and diseases live independently.
Camp Nurse
Camp nurses treat and assist children at summer camps or other organized group activities. Additionally, these specialists treat children with serious health problems, including HIV, cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, and other debilitating health conditions.
Cardiac Care Nurse
Cardiac care nurses specialize in heart problems and treating patients struggling with cardiac disease. Even though these specialists typically work in hospitals where heart surgery is performed, they frequently assist patients at home recovering from bypass surgery, pacemaker surgery, or an angioplasty. Additionally, they work with patients requiring medication or close monitoring.
Cardiac Cath Lab Nurse
Cardiac cath lab nurses assist doctors diagnosing heart problems and performing interventional treatments, such as valvuloplasties, angioplasties, and cardiac catheterizations. Additionally, these specialists assist cardiologists implanting cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), pacemakers, and other devices. Since technology is constantly changing, they must remain updated on new technologies and procedures.
Case Management Nurse
Nurses assigned case management duties organize and oversee long-term patient care, ensuring patients receive all necessary treatments and care. For example, case management nurses assigned cancer patients would be responsible for coordinating oncologist visits, radiation and surgical treatments, and post-treatment care. These nurses typically specialize in various areas, including pediatrics, oncology, cardiology, AIDS, chronic pain management, etc.
Clinical Nurse Leader
Clinical nurse leaders are licensed registered nurses who hold master’s degrees in nursing (MSN). This is a relatively new nursing specialty. Clinical nurse leaders are responsible for minimizing patient care errors administered in clinical environments. These specialists supervise patient care activities to ensure people receiving medical care are being treated with modern technology and procedures.
Community Health Nurse
Community health nurses are employed at non-profit organizations, medical clinics, government agencies, and various other settings. They specialize in health problems affecting populations, assist underprivileged individuals, and work with families requiring public assistance. They organize public campaigns and classes to teach preventative healthcare, nutrition, and raise awareness about public health problems. Additionally, they collaborate with elected officials, doctors, teachers, and parents to assist underprivileged populations and address public health problems.
Complementary Health Nurse
Complementary health nurses specialize in holistic medicine. They administer alternative healthcare treatments, such as massage therapy, acupuncture, and special nutrition plans.
Correctional Facility Nurse
Correctional facility nurses work in correctional facilities. They treat inmates imprisoned within prisons, county jails, penitentiaries, and juvenile homes.
Dermatology Nurse
Dermatology nurses assist dermatologists. They also teach patients being treated for or recovering from skin disease how to properly care for themselves.
Developmental Disability Nurse
Developmental disability nurses treat and assist people diagnosed with mental or physical disabilities.
Diabetes Nurse
Diabetes nurses treat and assist people struggling with health problems related to diabetes, a disorder affecting insulin production. They also specialize in the endocrine system which includes the reproductive glands, hypothalamus, parathyroids, pituitary thyroid, pineal body, and adrenals.
Domestic Violence Nurse
Domestic violence nurses assist and treat victims of domestic abuse. They are typically employed at battered women shelters, police departments, and medical clinics. Many conduct research and participate in public advocacy to reduce domestic violence. This profession is also referred to as violence prevention, elder abuse, and child abuse nursing.
Ethics Nurse
Ethics nurses specialize in ethical issues within the nursing profession. They frequently sit on ethics committees at hospitals, insurance companies, and other facilities and work at law firms.
Family Nurse Practitioner
Family nurse practitioners hold master’s degrees and are licensed as registered nurses. Before being permitted to practice, they must certify by passing a national test. These specialists diagnose disease, arrange for diagnostic and lab tests, and some are permitted to prescribe medications. Since family nurse practitioners treat and care for patients of all ages, they possess the skills and knowledge to diagnose and provide care for various diseases and injuries.
Flight/Transport Nurse
Flight/transport nurses administer intensive care to critically injured or ill patients being transported to hospitals via ambulance or helicopter. Additionally, these specialists provide care to patients in less critical conditions being transported long distances by aircraft.
Forensic Nurse
Forensic nurses collaborate with police officers and criminal investigators conducting criminal investigations. They’re frequently called upon to investigate homicides, sexual assaults, abuse, and other crimes. Additionally, they treat and assist crime victims.
Gastroenterology Nurse
Endoscopy nurses, commonly known as gastroenterology nurses, assist doctors and provide nursing care to people struggling with digestive system problems. Common problems they treat include reflux, bleeding, abdominal pain, and cancers affecting digestive system organs.
Genetics Nurse
Genetics nurses administer nursing care to individuals diagnosed with genetic problems and diseases. They administer screenings, identify potential problems, treat disease, and assist child, adult, and elderly patients struggling with genetic disorders.
Geriatric/Gerontological Nurse
Geriatric and gerontological nurses provide nursing care to the elderly. These specialists are in high demand since over half of all hospitalized patients are 65 or older. Geriatric and gerontological nurses are primarily employed within hospitals and assisted living facilities. They have extensive training to prepare them for elderly patient care and teaching their patients how to live independently.
Gerontological Nurse Practitioner
Gerontological nurse practitioners specialize in elderly patient care. They hold master’s degrees and are licensed as registered nurses. These specialists are trained to diagnose and treat chronic and acute medical conditions. They frequently utilize holistic treatments to treat patients struggling with physical and mental health problems.
Gynecology/Obstetric Nurse
Gynecology and obstetric nurses specialize in women’s reproductive health. They treat women with reproductive issues, assist doctors, and teach adult and elderly women about preventative healthcare. These nurses often specialize as labor and delivery and perinatal nurses.
Health Policy Nurse
Nurses specializing in health policy work as analysts. They typically hold doctorate degrees and conduct research. Because of their expertise, health policy nurses frequently consult with elected officials, school administrators, and others to educate them about how health problems affect the public.
Hematology Nurse
Hematology nurses provide nursing care to patients diagnosed with leukemia, sickle-cell, hemophilia, or other blood related disorders. Since patients with these types of diseases need special care, they teach family members how to care for their loved ones. These blood-related diseases typically share similar characteristics with cancer, so hematology nurses frequently specialize in oncology.
Holistic Nurse
Holistic nurses utilize various treatments, including modern medical procedures, massage therapy, and nutrition plans to help patients recover from medical, psychological, and spiritual problems. Holistic nurses educate patients, so they’ll be empowered to take charge of their health.
Home Health Care Nurse
Home healthcare nurses administer nursing care to patients within their homes. They treat people recovering from serious injuries, the permanently disabled and elderly patients living independently. These specialists are also referred to as visiting nurses. Their work has improved the lives of untold numbers of people.
Independent Nurse Contractor
Independent nurse contractors provide their services to healthcare clinics where nurses are outsourced. They typically bill hourly. Nurse contractors have various specialties, and they can contract at physicians’ clinics, rehabilitation centers, assisted living facilities, physical therapy facilities, and home healthcare companies.
Infection Control Nurse
Infection control nurses recognize and eliminate infectious diseases rampant within medical clinics and the community. They gather data, educate staff members, and develop procedures to control the spread of infectious disease. They specialize in STDs, HIV, tuberculosis, and other infectious diseases common during hospital stays.
Informatics Nurse
Nurses specializing in informatics specialize in information technology utilized to manage records and deliver healthcare services. They’re currently in demand since paper form records are being digitized. They work with automated systems and sophisticated computer networks. They’re responsible for teaching nurses and other medical professionals how to utilize information technology and ensuring medical facilities are wired with modern networks.
Infusion Nurse
Infusion nurses, also known as intravenous nurses, administer fluids and mediations and assist patients who rely on arterial catheters. In addition to administering fluids, infusion nurses identify potential infections and drug interactions, keep tabs on patients, and fix problems. These specialists are employed at assisted living facilities, hospitals, and home healthcare companies.
Lactation Consultant
Nurses specializing in lactation assist women currently breastfeeding or experiencing complications. In addition to nursing care duties, these specialists work with elected officials to make the workplace and public facilities accommodating to breastfeeding mothers.
Legal Nurse Consultant
Nurses who offer legal consulting services assist attorneys with medical negligence cases and evaluate medical records.
Life Care Planning Nurse
Nurses specializing in life care planning assist severely injured patients recovering from serious burns, head trauma, spinal cord injuries, and other serious injuries. They work with patients, their family members, doctors, and lawyers to develop plans designed to address healthcare costs, future treatments, and other issues affecting patients’ wellbeing. To effectively do this, they must understand what type of treatments and care patients with specific injuries require. Additionally, these nurses must advocate on patients’ behalf since they often struggle expressing themselves. These specialists frequently work outside of hospitals as consultants for government agencies, courts, and private companies.
Long-term Care Nurse
Long-term care nurses treat patients with chronic diseases or severe disabilities. They typically work with elderly and disabled individuals. Long-term care is also known as sub-acute care.
Managed Care Nurse
Managed care nurses specialize in preventative care. They teach patients how to properly take care of their health to minimize healthcare expenses. They work with managed care healthcare providers to reduce expenses and provide more efficient care.
Medical-Surgical Nurse
Medical/surgical nurses are licensed registered nurses employed in assisted living facilities, hospitals, and other medical clinics where patients preparing and recovering from surgery are housed. Additionally, they assist patients with chronic pain being treated with medication.
Military and Uniformed Service Nurse
Military nurses serve in the military and care for service members in the Marines, Navy, Air Force, and Army. They also work for public health agencies.
Neonatal Intensive Care Nurse
Neonatal intensive care nurses treat premature or ill infants. They also assist mothers with any assistance while their newborns receive treatment.
Neuroscience Nurse
Neuroscience nurses specialize in nervous system disorders. They treat people with spinal cord injuries, severe brain trauma, seizures, and other nervous system injuries or diseases.
Nurse Attorney
These nurses hold law degrees. They frequently represent doctors and other medical specialists in court and collaborate with elected officials to develop new policies.
Nursing Legistlator
These professionals work for municipal, state, and federal government agencies. They work closely with politicians to formulate health policies to address rising healthcare costs, expanding coverage to underprivileged individuals, and other important health issues.
Nursing Manager/Administrator
Nurse managers and administers are typically experienced managers with nursing administration or business degrees. These professionals hold high-level positions at hospitals and medical clinics. They’re responsible for overseeing hospital nursing operations.
Ophthalmic Nurse
Ophthalmic nurses treat patients struggling with vision problems, such as glaucoma, blindness, cataracts, and other vision disorders.
Otorhinolaryngology Nurse
Otorhinolaryngology nurses assist and treat patients being treated for ear, nose, and throat problems. They also prepare patients for surgery. This field is also referred to as head and neck nursing.
Pain Management Nurse
Pain management nurses evaluate, assist, and monitor patients suffering with chronic pain. Pain management is also known as the fifth vital sign. They teach patients proper pain management techniques and monitor patients during pain management treatments. Nurses specializing in pain management are considered advanced practice nurses and pain management specialists since they have completed graduate-level education. Many pain management specialists certify in advanced oncology and palliative care.
Pediatric Endocrinology Nurse
Pediatric endocrinology nurses treat children diagnosed with endocrine system disorders and provide support to their families. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Children with endocrine system problems often begin puberty later in life and struggle with weight problems, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances.
Perianesthesia Nurse
Perianesthesia nurses assist patients in recovery rooms recovering from sedation following surgery. They get patients ready for surgery, monitor sedated patients, and help patients recovering from anesthesia.
Perinatal Nurse
Perinatal nurses administer nursing care to pregnant women, women in labor, and new mothers. They also provide support to women’s family members. These nurses spend a lot of time teaching mothers about proper prenatal care, comforting women struggling through labor, and teaching women how to care for newborns. Perinatal nurses are also called OB nurses, women’s health nurses, postpartum nurses, and couplet care nurses.
Plastic Surgery Nurse
Nurses employed in plastic surgery clinics assist patients preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from plastic surgery. They assist plastic surgeons performing all types of surgeries, including facial reconstruction surgery, dermabrasion, rhinoplasty, and other elective and necessary procedures.
Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
Psychiatric nurses are also known as mental health nurse practitioners. These specialists have advanced training and are licensed as registered nurses. Psychiatric nurse practitioners administer various psychiatric treatments and access patients for mental health problems. They assist patients struggling to manage mental health problems, and they provide preventative mental healthcare by teaching patients how to properly manage stress. These specialists are employed at psychiatric hospitals, addiction rehabilitation centers, and private clinics.
Pulmonary Care Nurse
Pulmonary care nurses treat patients with lung problems, such as asthma, tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, and individuals being taken off ventilators. These nurses work within hospitals in critical care and intensive care units, but they also work with patients at home struggling with emphysema, lung cancer, and other lung diseases.
Quality Improvement Nurse
Nurses specializing in quality improvement are responsible for improving nursing care at hospitals and other medical facilities. To do this, they evaluate current procedures, conduct patient surveys, and interview staff members. Once assessments are completed, these professionals develop new policies to be implemented within intensive care units, assisted living facilities, oncology clinics, etc.
Radiology Nurse
Radiology nurses assist patients receiving radiation treatment and being diagnosed with radiation imaging technology, such ultrasound technology and MRIs. Radiology nurses are also called cardiac catheterization lab nurses.
Rehabilitation Nurse
Rehabilitation nurses assist disabled patients and those recovering from serious injuries live independently. They also provide support to family members with disabled loved ones. Rehabilitation nurses also work in assisted living clinics to care for people unable to live independently.
Reproductive Nurse
Nurses specializing in reproductive health provide medical care and education to individuals with reproductive disorders, fertility problems, and other reproductive issues. These specialists are primarily located at fertility clinics where families are matched with egg donors and couples struggling with fertility problems receive counseling.
Rheumatology Nurse
Rheumatology nurses specialize in and care for patients with rheumatoid diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Lyme disease, fibromyalgia, lupus, spondylitis, and myositis. These nurses are responsible for assessing blood work and responses to pain, treating flares and symptoms, counseling patients, and determining whether patients are responding to medication.
Rural Nurse
Nurses practicing in rural settings treat patients living in scarcely populated and isolated regions. Frequently, rural areas lack doctors and healthcare resources. As a result, nurses are often responsible for providing care to people living in rural areas. To encourage nurses to work in rural settings, government agencies often offer tuition and loan repayment assistance.
Sub-acute Nurse
These specialists offer comprehensive nursing care to individuals requiring hospitalization for acute injuries and diseases. Most the time, this type of care lasts longer than long-term and assisted living care, but shorter than acute treatments.
Substance Abuse Nurse
Nurses specializing in substance abuse work at rehabilitation clinics where people undergoing treatment for drug and alcohol addiction are housed. They supervise patients receiving medications, provide routine nursing care, and offer emotional support to recovering addicts.
Supplemental/Agency Nurse
Nurses employed at nursing agencies work temporarily at hospitals and other medical facilities with staffing shortages.
Surgical Nurse
Surgical nurses assist patients preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from surgery. The following are specialists in this field: scrub nurses, specialists who sterilize surgical tools; RN first assistants, specialists who administer patient care during surgery; and circulating nurses, specialists with patient care duties in non-sterile settings.
Telemetry Nurse
Telemetry nurses specialize in technology designed to measure blood pressure, EKGs, blood-oxygen levels, and heart rate. They’re responsible for linking patients to this technology. After patients are linked to the technology, data about vital signs appear on computer screens for nurses and doctors to review. Telemetry nurses are responsible for analyzing and making judgments from the data.
Telephone Triage Nurse
Telephone triage nurses offer support to patients and other individuals requiring medical information via telephone. They’re frequently required to make judgments about the type of assistance people need after brief conversations. Telephone triage nurses are trained to understand when people need immediate medical care so unnecessary ambulance and emergency responses are minimized.
Toxicology Nurse
Toxicology nurses assistant patients undergoing detox treatments and requiring medical assistance following poison ingestion. These specialists often monitor patients for extended periods of time, conduct diagnostic and lab tests, and assist doctors treating poison victims. Additionally, toxicology nurses teach people how to avoid being exposed to toxic chemicals and compounds. These specialists must work well under stress since they frequently respond to life and death emergencies.
Transcultural Nurse
Transcultural nurses provide nursing care to immigrants, foreign refuges, and minorities. They typically understand the cultural values and beliefs of foreign nationals, so they understand how to administer care in a way that does not violate cultural and religious values.
Transplant Nurse
Transplant nurses assist people preparing for, undergoing, and recovering from organ transplants. They also work with living-donors preparing for surgery and the family members of organ transplant recipients. Transplant nurses coordinate nursing care for people receiving transplants and recovering from surgery. They also teach patients how to maintain good health following an organ transplant.
Trauma Nurse
Trauma nurses administer emergency treatment and care to people being treated for severe injuries. They monitor vital signs and notify doctors when emergency and life-saving treatments are needed.
Triage Nurse
Triage nurses are typically assigned to emergency rooms. They’re responsible for accurately and rapidly determining the type of treatment patients admitted to emergency rooms require. To do this, they must have exceptional analytical and judgment skills. Triage nurses must also be able to work effectively under pressure.
Urologic Nurse
Urologic nurses provide nursing care to patients with urologic disorders and diseases. They respond to acute disorders and treat patients struggling with chronic pain. They conduct exams, assess results from diagnostic tests, assist urologists treating bladder disorders, including incontinence, and educate patients about preventive healthcare.
Veterans Affair Nurse
Nurses employed with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) work at veterans’ hospitals, outpatient clinics, assisted living facilities, and other medical clinics where veterans receive medical care. Various nursing specialists, including registered nurses, clinical nurse specialists, APNs, NAs, LPNs, and nurse anesthetists are employed by the VA. In addition to treating veterans with health problems, they teach those with permanent disabilities how to live independently. Many VA nurses provide hospice care.
Wound & Ostomy Nurse
Wound and ostomy nurses assist patients requiring medical care for stomas, draining wounds, pressure and vascular wounds, fistulas, and neuropathic wounds. Additionally, they teach patients requiring special medical assistance how to manage these health disorders.
About
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Submit a Resource



